目录
Spring
先看下spring.io
从配置管理到安全性、web应用程序到大数据处理,无论你的项目需要什么样的基础设施,总有一个 Spring Project 能帮助到你构建你的项目。从小处开始,只使用你需要的部分–Spring是模块化设计的。(翻译自spring-projects首页:https://spring.io/projects)

平时常用的Spring Framework
平时说的Spring,其实大部分意思是这个 project 而已,因为这个里面包含了最核心的"IoC container"部分。 Spring MVC是 Spring 的一个模块。

什么是Servlet
介绍 Spring MVC 之前我们先来看下 Servlet 是什么。
Java Servlet 是工业标准(standard)
有两个大的版本:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
3.0版本之后用了新的 artifactId。
什么是标准,标准就是接口,定义了流程,定义了规范。
Servlet Container
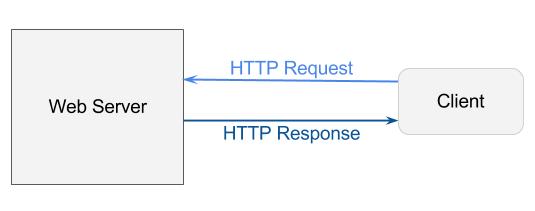
Web 服务器
Web 服务器使用 HTTP 协议来传输数据。最简单的一种情况是,用户在浏览器中输入一个URL(如,www.example.com/index.html),然后就能获取网页进行阅读。 因此,Web服务器完成的工作就是发送网页至客户端。传输过程遵循 HTTP 协议,它指明了请求(request)消息和响应(response)消息的格式。 用户/客户端只能向 Web 服务器请求静态网页。
Servlet 容器
Servlet 容器为处理每个请求分配独立的 Java 线程。 每一个 Servlet 都是一个拥有能处理 HTTP 请求并作出响应的 Java 类。 Servlet 容器的主要作用是将请求转发给相应的 Servlet 进行处理,并将动态生成的结果返回至客户端。 和所有的 Java 程序一样,Servlet 容器运行在 JVM 中。引入 Servlet 容器是为了处理复杂的 HTTP 请求。Servlet 容器负责 Servlet 的创建、执行和销毁。
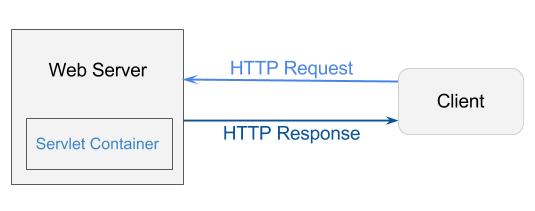
参考原文:https://www.programcreek.com/2013/04/what-is-servlet-container/
目前最流行的Servlet容器
Tomcat
Tomcat和IIS等Web服务器一样,具有处理HTML页面的功能,另外它还是一个Servlet和JSP容器,独立的Servlet容器是Tomcat的默认模式。 不过,Tomcat处理静态HTML的能力不如Apache服务器。
Jetty
Jetty 是一个开源的servlet容器,它为基于Java的web容器,例如JSP和servlet提供运行环境。Jetty是使用Java语言编写的, 它的API以一组JAR包的形式发布。开发人员可以将Jetty容器实例化成一个对象,可以迅速为一些独立运行(stand-alone)的Java应用提供网络和web连接。
Jboss
Jboss是一个基于J2EE的开放源代码的应用服务器。 JBoss代码遵循LGPL许可,可以在任何商业应用中免费使用。JBoss是一个管理EJB的容器和服务器, 支持EJB 1.1、EJB 2.0和EJB3的规范。但JBoss核心服务不包括支持servlet/JSP的WEB容器,一般与Tomcat或Jetty绑定使用。
Servlet 的配置方式
Servlet jar 包下有三个核心接口
配置的目的,是告诉容器构造哪些对象。
package javax.servlet;
import java.util.EventListener;
public interface ServletContextListener extends EventListener {
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce);
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce);
}
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Filter {
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException;
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException;
public void destroy();
}
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Servlet {
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
public String getServletInfo();
public void destroy();
}
方式1:2.5 标准的 web.xml
<web-app>
<listener>
<listener-class>com.gpengtao.web.listener.GptContextListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>requestLogFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>om.gpengtao.web.filter.requestLogFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>requestLogFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/gpt/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>showTime</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.gpengtao.servlet.ShowTimeServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>showTime</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/time/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
方式2:3.0 标准的注解

@WebListener
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
logger.info("<<<<<<<<<<<<<< My listener start <<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>> My lister end >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
}
}
@WebFilter(filterName = "myFilter", urlPatterns = "/*")
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) {
logger.info("<<<<<<<<<<<<< MyFilter 初始化, config={}", filterConfig);
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
logger.info("=================== do filter ===============");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>> destroy my filter >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
}
}
@WebServlet(name = "showTime", urlPatterns = "/time")
public class ShowTimeServlet extends HttpServlet {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ShowTimeServlet.class);
public ShowTimeServlet() {
logger.info("ShowTimeServlet constructed!");
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
logger.info("show time servlet receive request,uri:{}", req.getRequestURI());
resp.getWriter().write("ShowTime,现在时刻: " + new Date());
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
logger.info("ShowTime servlet 开始 init...");
super.init(config);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
logger.info("ShowTime servlet 开始 destroy...");
super.destroy();
}
}
方式3:SPI
认识 SPI
SPI,全名:Service Provider Interface,Java SPI具体约定:
当服务的提供者,提供了服务接口的一种实现之后,在jar包的META-INF/services/目录里同时创建一个以服务接口命名的文件。 该文件里就是实现该服务接口的具体实现类。而当外部程序装配这个模块的时候,就能通过该jar包META-INF/services/里的配置文件找到具体的实现类名, 并装载实例化,完成模块的注入。 基于这样一个约定就能很好的找到服务接口的实现类,而不需要再代码里制定。jdk提供服务实现查找的一个工具类:java.util.ServiceLoader。
定义接口:
package com.gpengtao.java.spi;
public interface SayHelloable {
void say();
}
定义两个实现类:
package com.gpengtao.java.spi;
public class SayChineseHello implements SayHelloable {
@Override
public void say() {
System.out.println("哈喽");
}
}
package com.gpengtao.java.spi;
public class SayEnglishHello implements SayHelloable {
@Override
public void say() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
在 /resources/META-INF/services 下建立文件 com.gpengtao.java.spi.SayHelloable 内容:
com.gpengtao.java.spi.SayEnglishHello
com.gpengtao.java.spi.SayChineseHello
运行测试类
package com.gpengtao.java.spi;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;
public class SPITest {
@Test
public void test() {
ServiceLoader<SayHelloable> loader = ServiceLoader.load(SayHelloable.class);
for (SayHelloable hello : loader) {
System.out.println(hello);
hello.say();
}
}
}
输出的结果是:
com.gpengtao.java.spi.SayEnglishHello@736e9adb
hello
com.gpengtao.java.spi.SayChineseHello@6d21714c
哈喽
Servlet 的 SPI
package javax.servlet;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Interface which allows a library/runtime to be notified of a web
* application's startup phase and perform any required programmatic
* registration of servlets, filters, and listeners in response to it.
*
* <p>Implementations of this interface may be annotated with
* {@link javax.servlet.annotation.HandlesTypes HandlesTypes}, in order to
* receive (at their {@link #onStartup} method) the Set of application
* classes that implement, extend, or have been annotated with the class
* types specified by the annotation.
*
* ......
*
* @since Servlet 3.0
*/
public interface ServletContainerInitializer {
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> c, ServletContext ctx) throws ServletException;
}
Spring MVC 做了什么
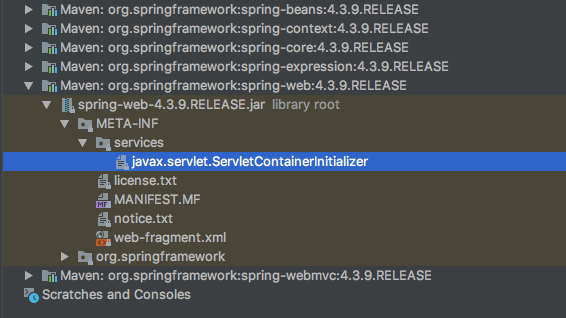
spring-web jar 包下配置了 SPI 文件,配置的接口是:org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer。
/**
* Servlet 3.0 {@link ServletContainerInitializer} designed to support code-based
* configuration of the servlet container using Spring's {@link WebApplicationInitializer}
* SPI as opposed to (or possibly in combination with) the traditional
* {@code web.xml}-based approach.
*
* ......
*
* @since 3.1
*/
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
/**
* Delegate the {@code ServletContext} to any {@link WebApplicationInitializer}
* implementations present on the application classpath.
* <p>Because this class declares @{@code HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)},
* Servlet 3.0+ containers will automatically scan the classpath for implementations
* of Spring's {@code WebApplicationInitializer} interface and provide the set of all
* such types to the {@code webAppInitializerClasses} parameter of this method.
* <p>If no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations are found on the classpath,
* this method is effectively a no-op. An INFO-level log message will be issued notifying
* the user that the {@code ServletContainerInitializer} has indeed been invoked but that
* no {@code WebApplicationInitializer} implementations were found.
* <p>Assuming that one or more {@code WebApplicationInitializer} types are detected,
* they will be instantiated (and <em>sorted</em> if the @{@link
* org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is present or
* the {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered Ordered} interface has been
* implemented). Then the {@link WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)}
* method will be invoked on each instance, delegating the {@code ServletContext} such
* that each instance may register and configure servlets such as Spring's
* {@code DispatcherServlet}, listeners such as Spring's {@code ContextLoaderListener},
* or any other Servlet API componentry such as filters.
* @param webAppInitializerClasses all implementations of
* {@link WebApplicationInitializer} found on the application classpath
* @param servletContext the servlet context to be initialized
* @see WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup(ServletContext)
* @see AnnotationAwareOrderComparator
*/
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<WebApplicationInitializer>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) waiClass.newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
Spring MVC
以下内容整理自官网。
参考:https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.1.5.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/index.html
Web on Servlet Stack
Spring Web MVC是基于Servlet API构建的原始Web框架,从一开始就被包含在Spring框架中。正式名称“Spring Web MVC”来自它的源模块(Spring-Web MVC)的名称,但是它通常被称为“Spring MVC”。
与许多其他web框架一样,Spring MVC是围绕前端控制器模式(front controller pattern)设计的,其中 DispatcherServlet 提供了一个共享的请求处理算法,而实际工作则由可配置的委托组件执行。
与任何Servlet一样,DispatcherServlet需要通过使用Java配置或在web.xml中声明和映射,并根据Servlet规范进行映射。反过来,DispatcherServlet使用Spring配置来发现它在请求映射、视图解析、异常处理等方面所需要的委托组件。
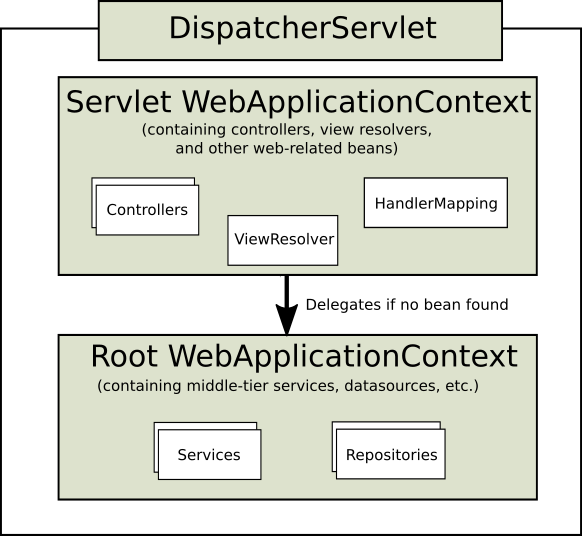
对于许多应用程序来说,拥有一个单一的WebApplicationContext是简单而足够的。 Spring Web Mvc 还支持上下文层次结构,其中一个 Root WebApplicationContext 跨多个 DispatcherServlet(或其他Servlet)实例共享。 Root WebApplicationContext 通常包含基础设施 beans,比如数据存储库和业务服务,它们可以跨多个 Servlet 实例被共享。 这些 beans 可以被继承,并且可以在特定于 Servlet 的子 WebApplicationContext 中复盖(即重新声明)。 下面的图片显示了这种关系:
配置
下面的web.xml配置示例注册并初始化了DispatcherServlet:
<web-app>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>app1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/app1-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>app1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/app1/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
基于Java代码(Java-based)的配置方式,spring推荐的方式。
下面的基于顶级接口 WebApplicationInitializer 配置 DispatcherServlet,它会被Servlet容器自动检测到:
import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer;
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
XmlWebApplicationContext appContext = new XmlWebApplicationContext();
appContext.setConfigLocation("/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml");
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(appContext));
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/");
}
}
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletCxt) {
// Load Spring web application configuration
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ac.register(AppConfig.class);
ac.refresh();
// Create and register the DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet servlet = new DispatcherServlet(ac);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletCxt.addServlet("app", servlet);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/app/*");
}
}
基于抽象类 AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 配置DispatcherServlet:
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
XmlWebApplicationContext cxt = new XmlWebApplicationContext();
cxt.setConfigLocation("/WEB-INF/spring/dispatcher-config.xml");
return cxt;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
还可以注册 Filter
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
// ...
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
return new Filter[] {
new HiddenHttpMethodFilter(), new CharacterEncodingFilter() };
}
}
基于抽象类 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer 配置DispatcherServlet:
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[] { MyWebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}